Local: Tomada de decisão do consumidor e gerenciamento de despesas
Objetivos de aprendizagem da lição:
Introdução:
This chapter focuses on consumer decision-making and managing expenses. By understanding financial behaviors and attitudes, as well as legal aspects of contracts and record organization, you will be better equipped to make informed financial decisions.
- Understand the legal implications of contracts in the EU. Learn how contracts, whether signed electronically or on paper, are legally binding. This knowledge helps you make informed decisions when entering agreements and avoid potential legal issues.
- Learn effective organization of financial records, both physically and digitally, to ensure easy access and retrieval. This will help you manage documents related to purchases, loans, and transactions, supporting financial planning and decision-making.
- Develop skills in managing expenses by identifying essential versus non-essential spending, setting budgets, and organizing payments. This helps maintain financial control and achieve short- and long-term goals.
- Gain awareness of digital security for financial records by understanding cloud storage risks and backup strategies. This ensures safe, secure, and cost-effective management of sensitive information.
Introdução
In managing personal finances, understanding both your financial attitudes and behaviors is crucial. The way we think about money and the decisions we make when handling it are often shaped by personal experiences, societal influences, and cultural norms. This chapter explores key aspects of financial attitudes and behaviors, including how consumers make decisions, manage contracts, and organize their financial records. You’ll also learn how values, biases, and relationships affect financial decisions, both locally in the EU and globally. Understanding these elements will empower you to make informed, thoughtful decisions that align with your financial goals.
2.1 Understanding Contracts and Legal Implications
In the EU, consumers must be aware of the legal implications of signing contracts, whether for purchasing assets, services, or products. Signing a contract, whether in paper form ou electronically, signifies a binding agreement with legal responsibilities. It’s important to read and fully understand the terms and conditions before agreeing, as they outline the rights, obligations, and potential penalties if the contract is breached.
In many EU countries, electronic signatures hold the same legal value as traditional signatures on paper. Therefore, individuals should exercise caution and ensure they are comfortable before signing contracts electronically.
Best Practice: If unsure about any terms, it is wise to seek legal or financial advice before signing, particularly for long-term commitments such as loans, rental agreements, ou mortgages. It is also a good practice to ask for clarification on any unclear terms or ask for errors to be corrected before finalizing the agreement.
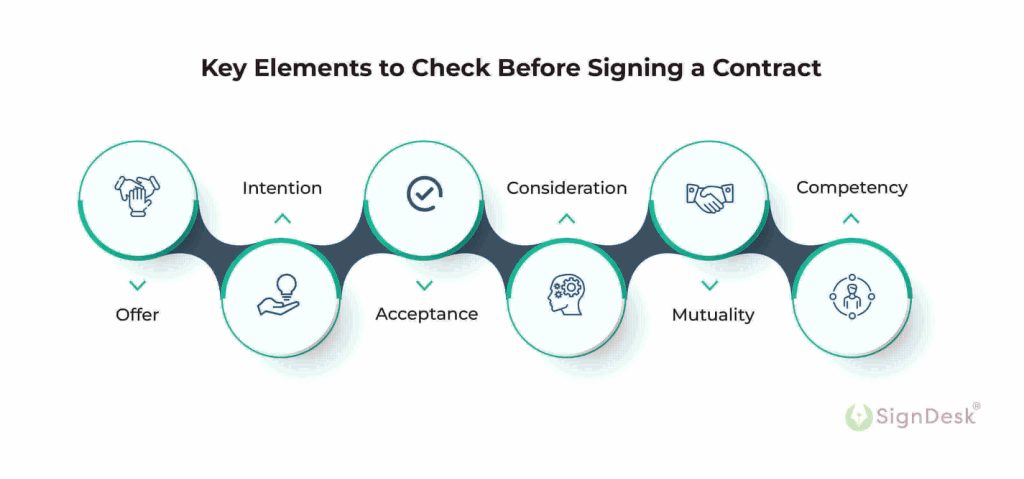
Figura: Key Elements to Check Before Signing a Contract
Descrição:
This figure illustrates the seven key elements that should be checked before signing a contract: Offer, Acceptance, Intention, Consideration, Mutuality, Competency, e Legal Compliance. Each element plays a crucial role in ensuring that the contract is valid, enforceable, and that both parties understand and agree to the terms. The process begins with an offer, followed by acceptance, and concludes when both parties demonstrate mutual understanding, competence, and consideration in the agreement.
Principais conclusões:
- Offer is the initial step where one party proposes an agreement.
- Acceptance confirms the other party agrees to the terms of the offer.
- Intention ensures both parties understand and agree to enter into a contract.
- Consideration refers to the value exchanged between the parties.
- Mutuality implies that both parties have agreed on the terms without any misunderstanding.
- Competency confirms that both parties are legally capable of entering a contract.
Aplicação da Informação:
Understanding these key elements is crucial when entering into a legally binding contract. By ensuring all elements are present and clear, individuals can protect themselves from potential legal disputes. This information is essential for both investors and learners to help them make informed decisions when negotiating and finalizing agreements.
2.2 Organizing Financial Records
Once a contract or financial agreement is signed, it’s crucial to organize and store these documents for future reference. Keeping records in an orderly and accessible way ensures that they can be easily retrieved when necessary. Important documents may include:
- Contracts for major purchases or services
- Receipts for significant transactions
- Invoices, bills, e loan agreements
For electronic contracts or records, cloud storage provides a convenient way to store documents securely and access them from any location. However, individuals should be aware of the security risks e cost implications of using cloud storage services. It’s important to choose secure platforms and consider encryption for sensitive data.
Keeping multiple backups, both physically and electronically, ensures that vital records are preserved in the event of data loss or theft.
2.3 Retrieving and Managing Documents
Having a well-organized system for retrieving documents is essential for maintaining control over personal finances. Whether documents are stored physically or digitally, individuals must be able to access them easily when needed, such as for tax purposes, verifying transactions, or resolving disputes.
If errors are found in financial records, consumers should immediately request corrections from the relevant parties. For example, a mistake on a loan agreement or an incorrect charge on an invoice should be rectified as soon as it is identified.
Additionally, consumers should always ask for written contracts or financial records when they are not provided. For significant purchases or services, keeping a written record is essential for resolving potential disputes.
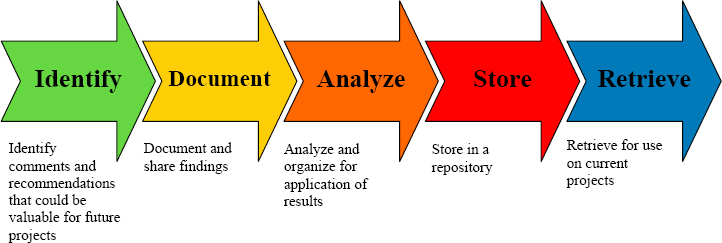
Figura: The Lessons Learned Process
Descrição:
This figure outlines a five-step process for managing lessons learned in project management. The steps are Identificar, Document, Analyze, Store, e Retrieve. Each step in the process is represented by an arrow and explains the activities involved: identifying valuable insights, documenting findings, analyzing the information, storing it in a repository, and retrieving it for future projects. This process ensures that valuable lessons from past projects are captured and used to improve future work.
Principais conclusões:
- Identificar: Find valuable comments and recommendations for future projects.
- Document: Share and record the findings for future use.
- Analyze: Review and organize the information for application.
- Store: Save the findings in a repository for easy access.
- Retrieve: Use the stored information for current or upcoming projects.
Aplicação da Informação:
This structured process helps individuals and teams make continuous improvements by leveraging lessons from previous projects. It is essential for investors and learners in any field to ensure that their experiences are well-documented and applied in future endeavors, thereby improving project outcomes and reducing risks.
2.4 Security and Cloud Storage
As more consumers move towards digital record-keeping, it’s important to understand the security risks associated with storing documents electronically, particularly on cloud storage platforms. While cloud storage offers convenience, users must consider the potential for data breaches ou hacking. Using secure, well-known providers and encrypting sensitive documents can help mitigate these risks.
In addition to security, the cost implications of using cloud storage need to be considered. While many providers offer free services for a limited amount of storage, larger volumes of data may require paid subscriptions.
Consumers should also make sure they have multiple backups of important financial records, ideally in both digital and physical formats, to ensure that they are protected from data loss.
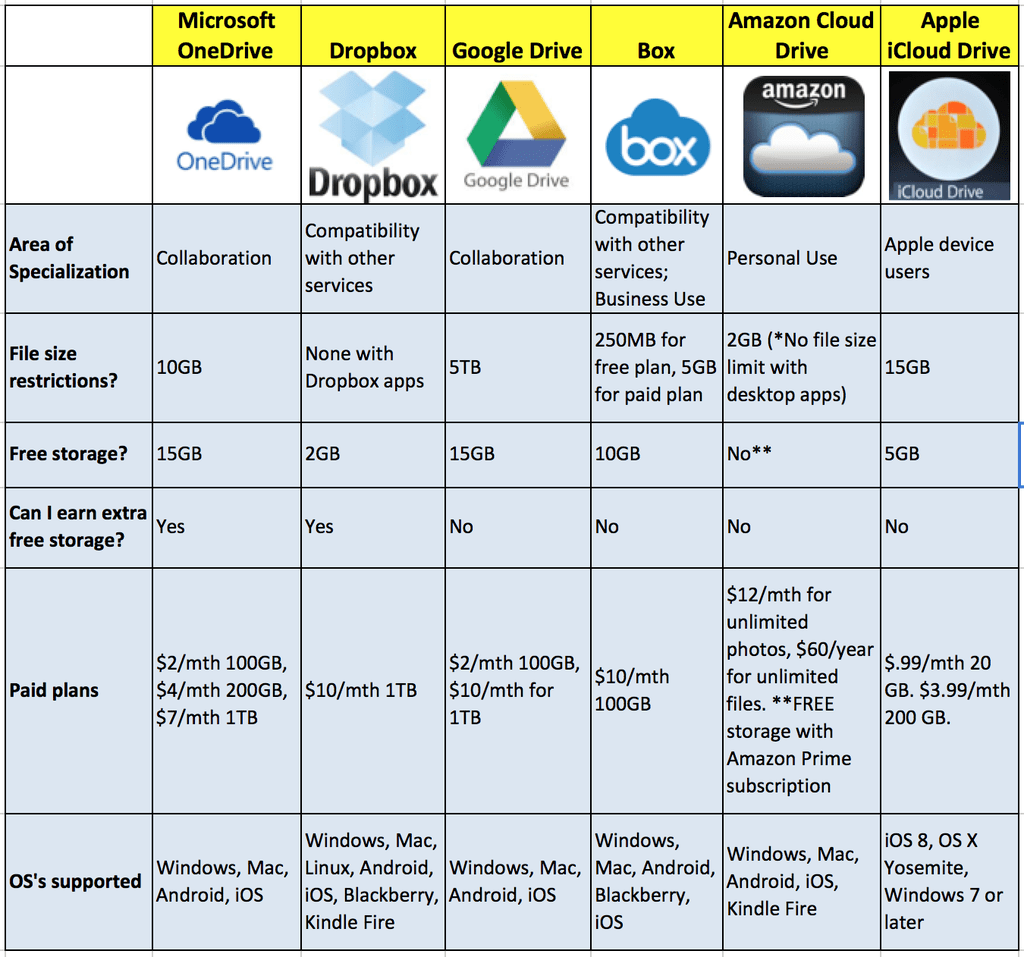
Figura: Cloud Storage Comparison
Descrição:
This chart compares five popular cloud storage providers: Microsoft OneDrive, Dropbox, Google Drive, Box, Amazon Cloud Drive, e Apple iCloud Drive. The table highlights their areas of specialization, file size restrictions, free storage amounts, ability to earn extra free storage, paid plans, and operating systems supported. Each provider offers different benefits for collaboration, personal use, or business purposes, along with various pricing and storage options, depending on user needs.
Principais conclusões:
- Microsoft OneDrive and Google Drive offer the most free storage at 15GB.
- Amazon Cloud Drive has a unique offering of unlimited photos for $12/month.
- Dropbox offers a compatibility advantage with other services.
- File size limits vary, with Google Drive offering up to 5TB per file.
- Operating systems supported are similar across most providers, with slight differences like iOS and OS X focus for iCloud.
Aplicação da Informação:
Understanding the differences in cloud storage providers can help investors and learners choose the right solution based on their needs. Whether for collaboration, personal storage, or extensive business use, the right plan offers value based on storage size, file limits, and compatibility with various devices. Comparing costs and services helps individuals and companies optimize their digital storage investments.
Informações importantes da lição:
- Contracts are legally binding agreements that require careful review. Ensure that you understand all terms before signing to protect yourself from legal disputes. If any terms are unclear, seek advice or request clarification before finalizing.
- Organizing financial records effectively makes it easier to retrieve important documents for tax purposes, verifying transactions, or resolving disputes. Use both digital and physical backups to ensure data is accessible and secure.
- Digital security is essential for protecting financial records stored in the cloud. Use reputable cloud providers, encrypt sensitive information, and maintain multiple backups to prevent data loss or unauthorized access.
- Managing expenses requires understanding needs and wants and setting a realistic budget. Prioritize essential spending, reduce unnecessary expenses, and regularly review your budget to stay financially stable.
- Effective decision-making includes considering both short- and long-term impacts of financial choices. Analyze options thoroughly, avoid impulsive purchases, and seek expert advice when needed to achieve better financial outcomes.
Declaração de Encerramento: By mastering contract management, record organization, expense tracking, and digital security, you can make informed financial decisions that align with your goals. Consistent application of these skills supports both short- and long-term financial success, ensuring a stable financial future.


