第 11 章:税务规划和策略(美国)
课程学习目标:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,consectetur adipiscing elit。 Ut elit tellus,luctus nec ullamcorper mattis,pulvinar dapibus leo。
11.2. Types and Impact of Taxes
根据收入来源、收入金额和消费习惯,征收不同类型和金额的税。例如,销售税被视为累退税,因为它从低收入者那里收取了更大比例的收入。
不同类型的收入征收不同的税,以促进公平、激励某些行为并支持各种政府服务。例如,长期资本收益的税率较低,以鼓励储蓄和投资。
- 例如:詹姆斯的年收入为 $50,000,而奥利维亚的收入为 $150,000,当他们都购买同一台价值 $1,000 的电视机时,他缴纳的销售税占收入的百分比要高于他。
所得收入:
工资或薪金等劳动收入需缴纳联邦所得税,税率从 10% 到 37% 不等,具体取决于个人所属的税级。
联邦所得税用于资助国家计划和服务,而州所得税用于资助州级计划。
工资税,例如社会保障税和医疗保险税,在联邦层面为各自的项目提供资金。
- 爱丽丝的工资为 $80,000,属于 22% 联邦所得税等级。如果爱丽丝收到 $2,000 合格股息和 $3,000 长期资本收益,则这些将按最高税率 15% 征税,前提是她不属于最高收入等级。她的工资将按 22% 之前的各种税率征税,但她的投资收入将征税较少,从而提高其税收策略的整体效率。
- Bob 是一名独立承包商,收入为 $50,000,他在附表 C 中申报。他的收入须缴纳自雇税,其中包括雇员和雇主缴纳的社会保障和医疗保险税以及所得税。Bob 可以选择向 SEP IRA 供款,这可以减少他的应税收入并提供退休储蓄。
非劳动收入:
来自投资的收入,例如股息、利息或资本收益。
利息收入:
利息收入通常来自储蓄账户或债券等投资,作为普通收入按与劳动收入相同的税率征税。
资本收益:
资本收益是出售股票或房地产等资产的利润。短期资本收益(持有时间少于一年的资产)作为普通收入征税,而长期资本收益的税率较低,通常为 0%、15% 或 20%,具体取决于您的收入水平。
税率比较:
资本收益等非劳动收入的税率与劳动收入不同,这通常会导致长期持有的投资纳税义务较低。
销售税:
销售税适用于大多数商品和部分服务。杂货和处方药等必需品通常免征,以减轻必需品的税收负担。
销售税通常由州和地方征收,用于资助州和地方政府的运营。
房产税:
财产税通常由地方政府征收,用于资助公立学校和紧急服务等当地服务。
赚取收入与资本收益
劳动所得通常按边际税率征税,这意味着随着收入的增加,税率也会通过税级增加。这种累进税制旨在确保收入较高的人为税基贡献更大的比例。
另一方面,资本利得通常以较低的税率征税,以鼓励对企业和股市的投资。这一优惠税率适用于持有一年以上的长期投资,反映了人们认为长期投资有助于经济增长的信念。
股票股息可以是合格的,也可以是非合格的,合格股息可享受与长期资本收益类似的较低税率。
- 1. 劳动收入情景:
- 人物:Jane,软件开发人员
- 年薪:$85,000
- 联邦所得税税率:她的税级为 24%
- 州税率:5%(她所在的州)
- FICA 税:7.65%(社会保障和医疗保险合计)
- 情景:简的净收入受到这些税款的影响,这些税款会自动从她的工资中扣除。如果她向 401(k) 或传统 IRA 缴款,她的应税收入可能会降低,因此缴纳的所得税也会减少。
- 2. 资本利得情景:
- 人物:投资者 Alex
- 股票出售收益:$20,000(持有一年以上)
- 联邦资本利得税率:15%(适合他的收入水平)
- 州税率:无(在他所在的州)
- 情景:Alex 出售持有一年多的股票。他从出售股票中获得的利润,即长期资本收益,按 15% 征税,而不是按正常所得税率征税,后者会更高。
11.3 Tax Forms and Payments
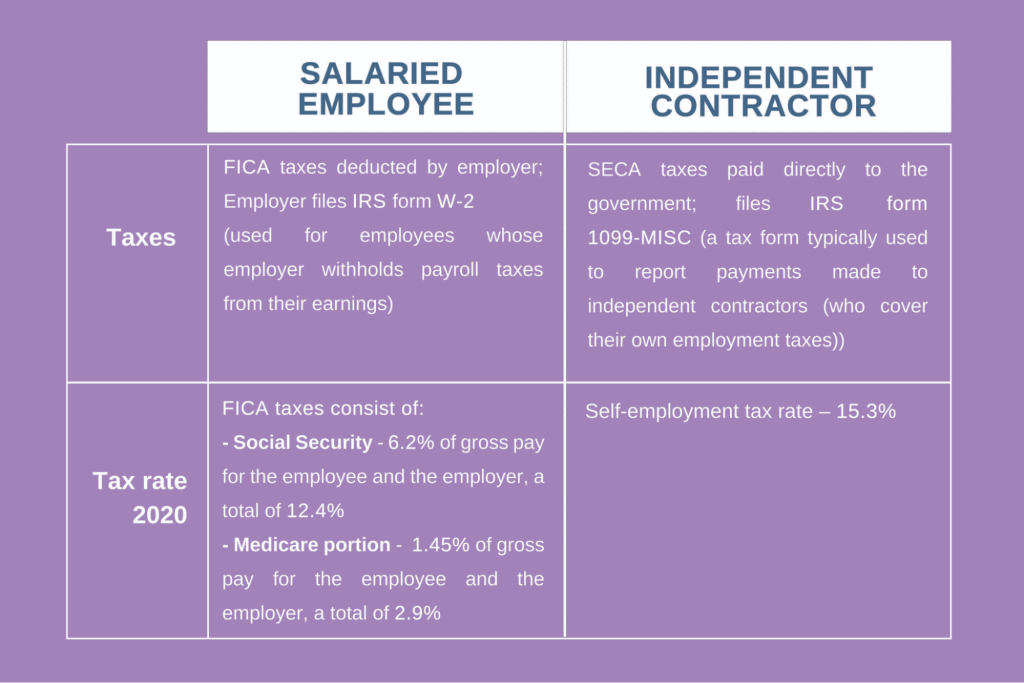
数字: 受薪雇员与独立销售代表:哪种方式最适合您的全球企业?
描述:
The infographic likely compares the benefits and challenges of hiring salaried employees versus independent sales representatives for global enterprises. It may outline key factors such as cost, flexibility, control, and scalability, providing insights into how each option fits different business needs and objectives.
要点:
- 受薪雇员和独立销售代表的成本效益可能存在很大差异,后者通常需要较少的前期投资。
- 独立销售代表的灵活性和可扩展性通常更高,使企业能够更快地适应市场变化。
- 受薪员工对品牌代表和销售策略的控制通常更强。
- 两者之间的选择取决于公司的战略目标、预算和市场动态。
信息应用:
Understanding the pros and cons of each employment model is crucial for businesses expanding globally. Companies must assess their operational needs, growth strategies, and the level of control desired over sales processes to make an informed decision. This analysis is particularly useful for HR professionals, business strategists, and decision-makers planning to scale their operations internationally or optimize their sales force.
1040 等税表允许个人计算联邦所得税。个人是否会获得退税或需要额外缴纳税款取决于其纳税年度的预扣税和抵免额。
- 示例:Jacob 填写完 1040 表后,意识到自己因预扣税款过多而多缴了税款,并且有资格获得退款。
W-4 表格:
开始工作时,员工需要填写 W-4 表格,告知雇主应从其工资中扣除多少税款。此表格会考虑员工的报税状态、多份工作以及他们希望申请的任何扣除或抵免。
示例:爱丽丝可能会在她的受薪工作中调整她的 W-4,以确保预扣正确的税额,避免少付罚款或年底的大额税单。
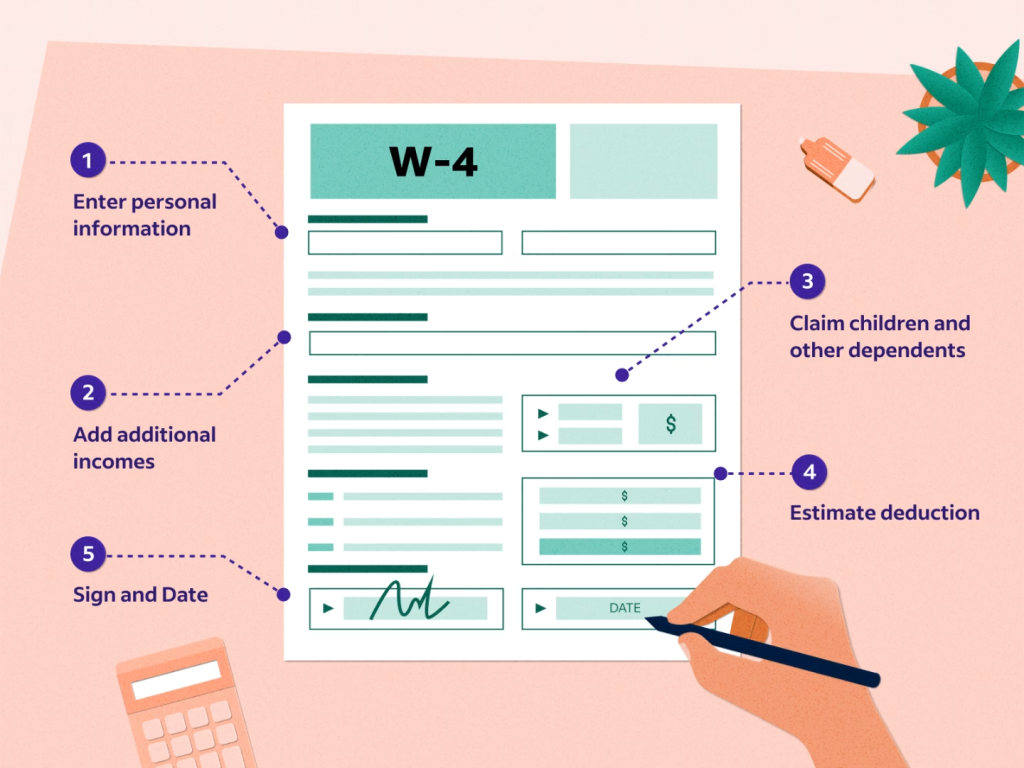
数字: 了解 W-4 表格上应申报什么内容
描述:
The infographic likely provides a visual guide on how to fill out a W-4 form, which is essential for determining the amount of federal income tax withheld from your paycheck. It may include sections on personal information, multiple jobs or spouse’s income, dependents, other adjustments, and a final declaration. The goal is to help employees claim the correct withholding amount to avoid owing taxes or receiving a large refund at the end of the tax year.
要点:
- W-4 表格对于设置您的税收预扣以匹配您的纳税义务至关重要。
- 申请津贴的方法已经被一种更直接的方法来计算抵免和扣除额所取代。
- 准确报告收入和扣除额有助于实现平衡的税收状况,避免少付或多付。
- 该表格包括额外收入、扣除额和额外预扣税部分,以根据您的纳税义务确定预扣税金额。
信息应用:
Properly filling out a W-4 can significantly impact your financial planning by ensuring that your paycheck reflects your actual tax obligations as closely as possible. It’s particularly important for those with multiple jobs, significant non-wage income, or various deductions and credits. Understanding how to navigate this form can help employees manage their tax burden more effectively, leading to better financial health and planning.
表格 1040:
在纳税年度结束时,个人填写 1040 表以计算其实际纳税义务。根据所欠税款总额以及已通过预扣税或预估税支付的税款,纳税人将获得退税或欠缴额外税款。
示例:独立承包商在附表 C 中报告收入,且不扣缴税款,因此需要他们按季度缴纳预估税款。
示例:鲍勃的 1040 表将包括他的 C 表收入,并且除了所得税之外,他还需要计算自雇税。
数字: 填写 IRS 表格 1040 的分步指南
描述:
The infographic likely offers a visual step-by-step guide on how to correctly fill out IRS Form 1040, which is the standard federal income tax form used to report an individual’s gross income. It might include sections on personal information, income details, deductions to claim, and how to calculate the tax owed or refund due. The aim is to simplify the process of tax filing for individuals by breaking down each part of the form into manageable steps.
要点:
- IRS 表格 1040 对于报告年度收入、计算应缴税款以及申请扣除额和抵免额至关重要。
- 准确填写表格可确保遵守税法,并有助于最大限度地获得合法扣除和抵免。
- 了解表格的每个部分可以减少错误和审计的可能性。
信息应用:
Properly filling out IRS Form 1040 is crucial for all taxpayers. This knowledge helps in navigating the complexities of tax laws and regulations, ensuring that individuals pay the correct amount of taxes. It’s particularly beneficial for those looking to understand their tax obligations better, plan for tax season, and avoid common pitfalls in tax preparation.
11.4 Involuntary vs. Voluntary Deductions
非自愿扣除: 这些都是强制性的,包括联邦、州和地方税、社会保障和医疗保险。
自愿扣除: 这些都是可选的,包括退休账户捐款和慈善捐款。
工资税:
工资税会自动从员工的工资中扣除,其中包括社会保障和医疗保险缴款。
税收抵免与税收减免:
税收抵免可逐一减少应纳税额,而减免则可减少应纳税所得额。税收抵免可以是可退还的,也可以是不可退还的。
- 扣除示例:如果 Alice 的可扣除费用为 $1,000,并且她属于 22% 税级,则此项扣除可为她节省 $220 的税款($1,000 * 22%)。
- 抵免示例:如果鲍勃有资格获得 $1,000 的税收抵免,那么他的纳税义务就会一一减少,因此,无论他的税级如何,他都要少缴纳 $1,000 的税款。
税收抵免示例:
- 儿童税收抵免(可退还)
- 美国机会税收抵免(部分可退还)
- 终身学习积分(不可退还
11.5 Local Taxation
地方税用于资助城市或县级项目。例如,不同县的财产税可能有所不同,通常用于资助当地学校和公共工程。
- 示例:莎拉缴纳的房产税率比隔壁县的表妹高,因为莎拉所在的县最近对道路进行了大规模改造。
11.6 Calculating Taxes
计算税款需要了解各种因素,包括收入金额和购买类型。联邦所得税是累进税,这意味着收入水平越高,税额就越高,而销售税对每个人的税率都相同,无论收入多少。
- 示例:自由摄影师诺亚 (Noah) 的收入边际税率比他的助手高,因为他的收入等级较高。
收入和支出的税收示例
收入来源 | 数量 | 联邦税率 | 州税率 | 已付销售税 |
薪水 | $60,000 | 22% | 6% | $600 |
兴趣 | $500 | 22% | 6% | 不适用 |
资本利得 | $2,000 | 15% | 0% | 不适用 |
示例:约翰的工资为 $60,000,利息收入为 $500,股票销售利润为 $2,000。他的总纳税义务将根据这些金额计算,并根据他的支出和适用的州税进行调整。
Tax Benefits and Incentives
税收优惠(如减税和抵免)可减少纳税义务,并可显著影响个人财务状况。抵免可直接减少应纳税额,而减税可减少应纳税所得额。
- 示例:米娅向 401(k)计划供款,这减少了她的应税收入,并为她带来了即时的税收优惠。
Tax-Affected Investments
根据持有期限和收入类型,投资需接受不同的税收处理。例如,长期资本收益的税率低于短期收益。
- 示例:卡洛斯出售了持有一年以上的股票,享受长期资本利得税率,该税率低于短期收益税率。
Taxpayer’s Filing Obligations
所有受雇个人都必须每年向美国国税局报告其收入,这通常会导致多缴税款的退税或预扣税款不足的应付税款。
- 示例:Lila 是一名教师,她在申报纳税后发现,由于各种教育抵免,她需要向美国国税局 (IRS) 申请退款。
一、地方税务差异
地方税(例如用于学校资金或基础设施的税)因城市而异,反映了每个社区独特的需求和决定。
- 示例:马克居住在一个房产税较高的城市,因为该城市优先考虑公立学校的资金。
11.7 Tax Credits and Deductions
了解并利用税收抵免和减免可以节省大量开支。例如,教育抵免可以降低学生的税单,而抵押贷款利息减免可以使房主受益。
- 示例:Zoe 是一名刚毕业的大学毕业生,她申请了教育抵免以减少她一年内支付的学费的纳税义务。
Pre-Tax Savings
对退休账户的税前供款可减少当前应税收入,并延迟纳税,直至提取资金,退休期间的税率通常较低。
爱尔兰共和军:
- 传统 IRA: 捐款可以免税,并且收益增长在提取前可以延税。
- 示例:安德烈向传统 IRA 缴纳了款项,这降低了他当前的应税收入,从而有可能使他进入较低的税率等级。
- 如果鲍勃有传统的个人退休账户 (IRA),他的缴款可能会降低他当前的应税收入,但他将为退休时提款缴纳税款。
- 罗斯个人退休账户(Roth IRA): 捐款以税后美元支付,但收益和提款免税。
- 例如:如果鲍勃有传统 IRA,他的缴款可能会降低他当前的应税收入,但他退休时提款时需缴税。
传统 IRA 与罗斯 IRA:如果艾丽丝现在想减少她的应税收入,她可能会向传统 IRA 供款,而如果她预计退休时会处于更高的税率等级,她可能会选择罗斯 IRA 来实现免税增长和提款。
教育储蓄账户:
- 教育储蓄账户: 这些账户为教育费用储蓄提供了税收优惠。
- 税收优势比较: 爱丽丝考虑为孩子的教育开设一个 529 计划。这些捐款不能享受联邦税收减免,但收入增长免税,符合条件的教育费用提款也免税。
税务规划:
税务规划至关重要。它需要了解税法的复杂细节以及不同类型的收入和扣除额如何影响纳税义务。战略规划可以优化纳税状况,并可能随着时间的推移节省大量资金。
11.8 Estate Planning Essentials
Estate planning ensures that an individual’s assets and healthcare wishes are carried out after their death or in cases where they are incapacitated.
- Wills specify how assets will be distributed and appoint guardians for minor children.
- 例子: Mia writes a will designating her sister as the guardian for her two young children.
- 例子: Mia writes a will designating her sister as the guardian for her two young children.
- Beneficiary Designations on retirement accounts, life insurance, and bank accounts dictate who will receive funds directly.
- 例子: Jason names his spouse as the primary beneficiary on his 401(k) account.
- 例子: Jason names his spouse as the primary beneficiary on his 401(k) account.
- Powers of Attorney (POA) authorize a trusted person to act on your behalf for financial or medical decisions if you become incapacitated.
- 例子: David assigns his brother medical POA to make health decisions if he is unable to.
- 例子: David assigns his brother medical POA to make health decisions if he is unable to.
应用:
Setting up a basic estate plan, even for young individuals, helps protect their interests and ensure loved ones are cared for according to their wishes.
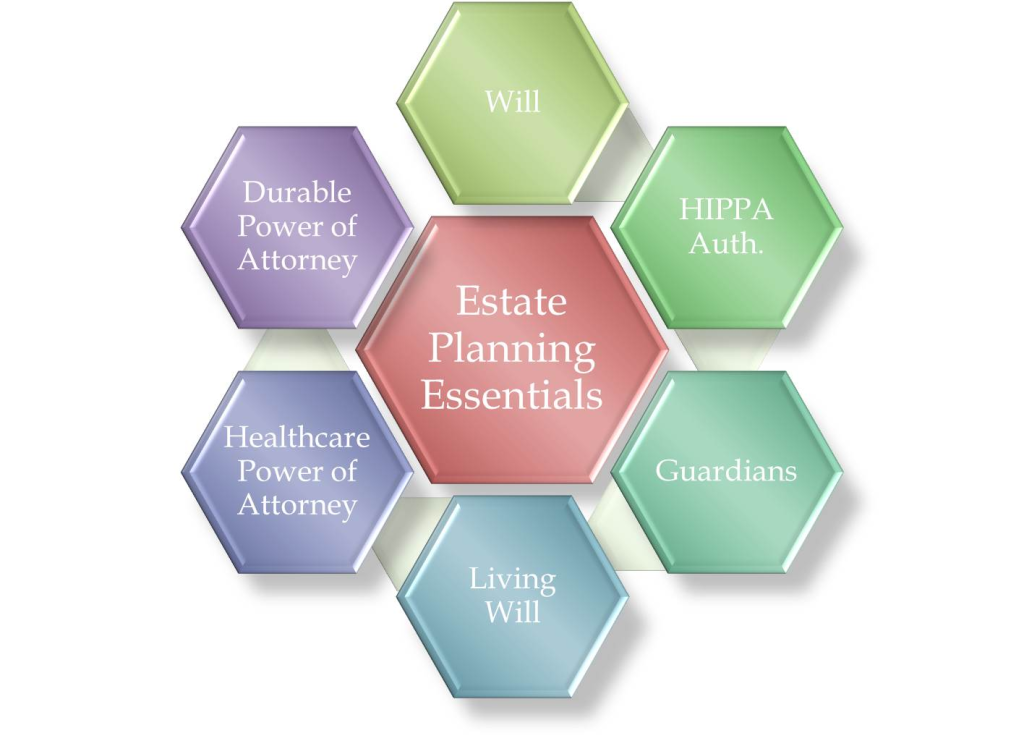
数字: The Core Components of an Estate Plan
描述:
This image outlines the foundational elements of a basic estate plan, showcasing the essential legal documents required to manage your assets and healthcare wishes. It likely highlights key components such as a Last Will and Testament, Power of Attorney, and healthcare directives. The goal is to show that estate planning is a critical process for everyone, regardless of wealth.
要点:
- Estate planning is the process of creating a plan for how your assets will be managed and distributed after your death or if you become incapacitated.
- A Last Will and Testament is a fundamental document that specifies who receives your property and who would act as a guardian for any minor children.
- A Durable Power of Attorney for finances and a Healthcare Power of Attorney are crucial documents that appoint someone to make decisions for you if you are unable to do so yourself.
- A well-structured estate plan can help your loved ones avoid probate, which is the often lengthy, costly, and public court process for settling an estate.
信息应用:
- This framework serves as a clear guide to the essential documents everyone should have in place to create a comprehensive estate plan.
- Proactively setting up these documents is a critical step to protect your family from unnecessary stress and financial complications during an already difficult time.
- It is important to review and update your estate plan every few years or after major life events like marriage, childbirth, or divorce to ensure it continues to reflect your wishes.
11.9 Historical Perspective on Income Tax Rates (1950–Present)
Tax rates in the United States have shifted significantly over time:
- 1950s: The top federal income tax rate was over 90% for the wealthiest Americans.
- 1980s (Reagan era): Tax reform lowered the top rate to 28% by the end of the decade.
- 2000s–Today: Rates fluctuate between 35% and 37% for high earners, with graduated brackets for middle and lower incomes.
应用:
Understanding historical tax rates highlights how tax policy impacts different income groups over time and can influence economic growth, consumer spending, and savings behavior.
Progressive vs. Regressive Taxes
- Progressive Taxes: Tax rates increase as income increases.
- 例子: Federal income tax — higher earners pay a higher percentage.
- 例子: Federal income tax — higher earners pay a higher percentage.
- Regressive Taxes: Tax rates take a larger percentage of income from low-income earners.
- 例子: Sales tax — a flat rate that impacts low-income earners more heavily.
- 例子: Sales tax — a flat rate that impacts low-income earners more heavily.
应用:
Knowing the difference between tax structures helps consumers advocate for policies aligned with their economic interests.
When to Adjust Your W-4
Major life changes may require adjusting tax withholding:
- Marriage or divorce
- Birth or adoption of a child
- Major salary change
- Purchase of a home
- Large medical expenses or deductions expected
例子:
After getting married, Olivia updates her W-4 to account for her spouse’s income and new standard deduction filing jointly, preventing underpayment at tax time.
主要课程信息:
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,consectetur adipiscing elit。 Ut elit tellus,luctus nec ullamcorper mattis,pulvinar dapibus leo。