Local: analyzing European companies
课程学习目标:
- Learn about the income statement under IFRS. You will understand how revenues, 开支, 和 net income are reported, along with the inclusion of other comprehensive income (OCI). This helps investors assess a company’s profitability and financial performance.
- Understand the balance sheet under IFRS. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, 和 equity, offering insights into the company’s financial position. Learn about the distinctions between current and non-current items and how they reflect a company’s liquidity and solvency.
- Explore the cash flow statement under IFRS. The cash flow statement outlines how cash is generated and used across operating, investing, 和 financing activities. You will learn how this statement helps assess a company’s liquidity and its ability to generate cash to fund operations and investments.
- Gain insights into the overall structure and application of IFRS in European financial reporting. Understanding IFRS helps ensure transparency and comparability, making it easier to analyze financial statements and make informed investment decisions across borders.
介绍
Understanding the core financial concepts is essential for any investor. Financial statements provide critical insights into a company’s financial health and performance, helping investors evaluate profitability, liquidity, and growth potential. This section will introduce the fundamental financial statements—损益表, 资产负债表, 和 cash flow statement—and explain how to analyze these documents. We will also discuss key financial data points that investors use to assess a company’s performance.
22.1 Financial Statements
When analyzing European companies, it’s essential to understand that their financial statements are typically prepared according to the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), a global accounting framework that ensures transparency and comparability across borders. In Europe, IFRS is mandatory for all publicly listed companies, providing investors with consistent and clear financial information. This section introduces how financial statements in Europe adhere to IFRS, ensuring high-quality reporting.
IFRS and Income Statement
Under IFRS, the 损益表 (also called the statement of comprehensive income) follows a structured approach, similar to financial statements globally, but with some unique European nuances. The income statement provides detailed insight into a company’s revenues, costs, and overall profitability.
- Revenue Recognition: Under IFRS, revenue is recognized when control of a product or service is transferred to the customer. European companies must adhere to these rules, ensuring that revenues are reported accurately based on performance obligations, not just when payments are received.
- 营业费用: Expenses are classified by either their nature (e.g., wages, materials) or their function (e.g., cost of sales, administrative expenses). This flexibility allows European companies to present their income statements in a way that best reflects their operational structure.
- Other Comprehensive Income: IFRS emphasizes the importance of other comprehensive income (OCI), which includes gains or losses not reflected in the net income, such as foreign exchange differences or revaluation of financial instruments. This is particularly relevant for European companies operating in multiple currencies.
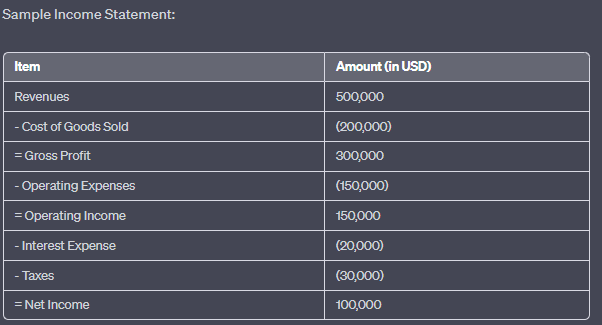
数字: 损益表样本
描述:
The image presents a sample income statement, breaking down the financial performance of a company over a specific period. It starts with the total revenues and subtracts various expenses to arrive at the net income. The statement showcases the following items:
收入:$500,000
销售成本:$(200,000)
毛利:$300,000
运营费用:$(450,000)
营业收入:$150,000
利息支出:$(20,000)
税:$(30,000)
净收入:$100,000
要点:
- 收入:扣除任何费用之前公司获得的总收入。
- 销售成本(COGS): 生产所售商品的直接成本。
- 毛利:公司从总收入中扣除销货成本后获得的利润。
- 营业费用:与日常业务运营相关的成本。
- 营业收入:业务运营利润(息税前利润)。
- 利息费用:借入资金的成本。
- 税费:根据公司应税收入向政府支付的金额。
- 净利:公司收入扣除所有费用后的总利润。
信息应用:
损益表是一份基本的财务文件,它为投资者和利益相关者提供公司在特定时期盈利能力的洞察。通过分析损益表,人们可以了解公司的收入来源、成本结构和整体财务状况。这些数据对于做出明智的投资决策和评估公司的运营效率至关重要。
22.2 IFRS and Balance Sheet (Statement of Financial Position)
这 资产负债表, known under IFRS as the statement of financial position, provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity. IFRS requires companies to clearly differentiate between current and non-current items to offer a transparent view of a company’s financial health.
- Asset Classification: European companies report assets as either current or non-current. Current assets include items like cash, receivables, and inventory, while non-current assets encompass long-term investments such as property, plant, and equipment (PPE), as well as intangible assets like goodwill.
- 负债: Under IFRS, liabilities are also divided into 当前的 (due within a year) and non-current. European companies must report their obligations, including debt, leases, and pensions, in this format, providing clear insights into their short-term and long-term obligations.
- Shareholders’ Equity: The shareholders’ equity section under IFRS is structured to show both contributed capital (from shareholders) and retained earnings (profits that have been reinvested into the business). European firms must also disclose other reserves, including revaluation reserves and foreign currency translation adjustments.
- Asset Classification: European companies report assets as either current or non-current. Current assets include items like cash, receivables, and inventory, while non-current assets encompass long-term investments such as property, plant, and equipment (PPE), as well as intangible assets like goodwill.
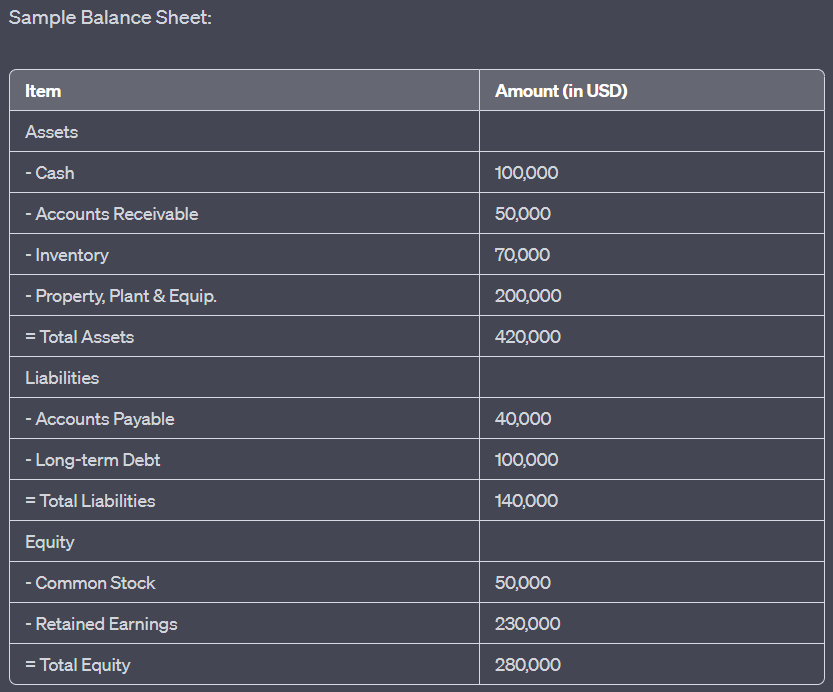
数字: Sample Balance Sheet
描述:
The image displays a sample balance sheet, which provides a snapshot of a company’s financial position at a specific point in time. It categorizes the company’s resources (assets) and the claims against those resources (liabilities and equity). The balance sheet showcases the following items:
- 资产: 总计 $420,000,包括现金($400,000)、应收账款($50,000)、存货($70,000)和财产、厂房和设备($200,000)。
- 负债: 总计 $140,000,包括应付账款($40,000)和长期债务($400,000)。
- 公平: 总计 $280,000,其中包括普通股($50,000)和保留收益($230,000)。
要点:
- 资产: 公司拥有的具有经济价值的资源。
- 负债:公司对外部实体承担的义务。
- 公平: 代表公司所有者权益,包括股东投入的资金和累计利润。
- 基本会计等式:资产=负债+权益。
会计等式:
\[ \displaystyle \text{资产} = \text{负债} + \text{权益} \]
\(\textbf{图例:}\)
资产 = 总资产
负债 = 总负债
权益 = 总权益
信息应用:
A balance sheet is a foundational financial statement that offers insights into a company’s financial health. By analyzing the balance sheet, stakeholders can assess the company’s liquidity, solvency, and overall financial stability. This information is vital for investors, creditors, and other stakeholders to make informed decisions related to the company’s financial position
22.3 IFRS and Cash Flow Statement
这 cash flow statement under IFRS follows a similar structure to other global standards but places particular emphasis on transparency in how cash is generated and used by the company. European companies use this statement to report cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities.
- 经营活动: IFRS allows for flexibility in reporting cash flows from operating activities, either through the direct method (showing cash receipts and payments) or the indirect method (starting with net income and adjusting for non-cash items). Most European companies opt for the indirect method.
- Investing and Financing Activities: Cash flows related to investments in assets or securities and activities such as issuing shares or repaying debt are reported here. European companies must clearly distinguish these transactions to show how they are funding their growth and managing their financial obligations.
- Foreign Exchange Impacts: Given that many European companies operate across multiple countries and currencies, IFRS requires the inclusion of cash flow impacts due to changes in foreign exchange rates, providing investors with a clearer understanding of how currency movements affect a company’s cash position.
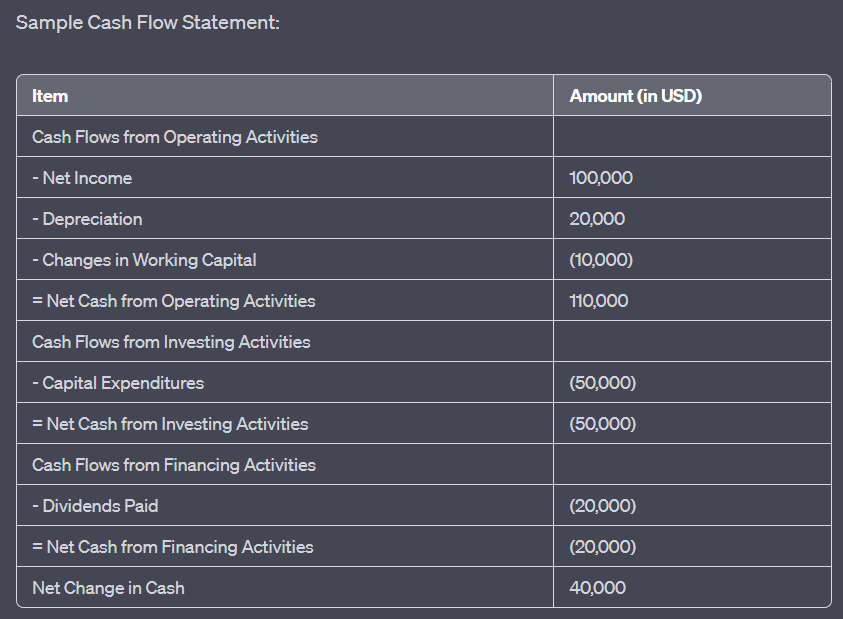
数字: Sample Cash Flow Statement
描述:
The image illustrates a sample cash flow statement, which provides a detailed account of the cash inflows and outflows for a company over a specific period. The statement is segmented into three main categories: Operating Activities, Investing Activities, and Financing Activities. The key items include:
经营活动产生的现金流量:净收入($100,000)、折旧($20,000)和营运资本变化(-$10,000),导致经营活动产生的净现金为 $110,000。
投资活动产生的现金流量: 资本支出(-$50,000),导致投资活动净现金为-$50,000。
融资活动产生的现金流量: 已支付股息(-$20,000),导致融资活动产生的净现金为-$20,000。
现金净变化总额为 $40,000。
要点:
- 经营活动:反映核心业务运营产生或使用的现金。
- 投资活动:表示用于投资资产或出售资产所收到的现金。
- 融资活动:展示来自或流向外部融资来源(如贷方和股东)的现金流。
- 现金净变化反映了公司一段时间内现金状况的总体增加或减少情况。
信息应用:
The cash flow statement is an essential financial tool that offers insights into a company’s liquidity and its ability to generate and use cash effectively. By analyzing the cash flow statement, stakeholders can understand how a company manages its cash resources, which is crucial for assessing its financial health and making informed investment decisions.
结论
In Europe, financial statements are prepared according to IFRS, ensuring a high level of consistency, transparency, and comparability across countries and industries. The 损益表, 资产负债表, 和 cash flow statement under IFRS provide investors with the detailed information needed to assess the financial health of European companies. IFRS’s global standards ensure that European companies’ financial reports meet international expectations, making it easier for investors to analyze and compare firms operating in different regions.
主要课程信息:
- The income statement shows a company’s profitability. The income statement provides a breakdown of a company’s revenues, cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, 和 net income. By analyzing this statement, investors can evaluate how efficiently a company is generating profits and managing costs. Revenue recognition under IFRS ensures accurate reporting based on performance obligations.
- The balance sheet offers a snapshot of a company’s financial position. It categorizes a company’s assets, liabilities, 和 equity. By examining these elements, investors can assess a company’s 流动性 (ability to meet short-term obligations), solvency (ability to meet long-term obligations), and financial health. The fundamental accounting equation of assets = liabilities + equity is key to understanding this statement.
- The cash flow statement tracks how cash is used. The statement divides cash flows into operating, investing, 和 financing activities. By analyzing this statement, investors can understand how the company generates cash from its operations, how it funds investments, and how it manages external financing. Positive cash flow from operating activities signals a strong cash position.
结语:
Financial statements under IFRS provide essential insights into a company’s financial health and performance. By analyzing the 损益表, 资产负债表, 和 cash flow statement, investors can make well-informed decisions based on transparency, consistency, and detailed reporting, helping them assess the company’s profitability, liquidity, and long-term sustainability.

